Intro to Information Technology FBLA provides a comprehensive overview of the field, equipping students with the foundational knowledge and skills necessary to excel in the digital age.
This guide explores the core components of information technology, including hardware, software, and networks, while emphasizing their practical applications and the ethical and legal considerations that shape the field.
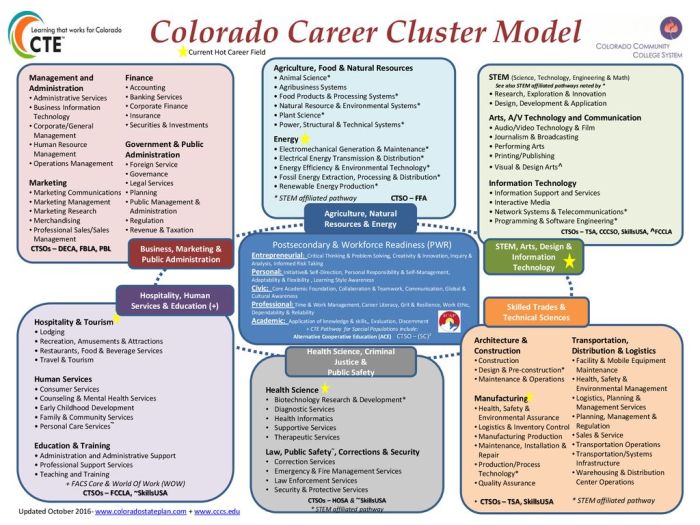
Introduction to Information Technology
Information technology (IT) is the study, design, development, implementation, support, and management of computer-based information systems. It is a rapidly growing field that is constantly changing as new technologies emerge.
IT is essential to the modern world. It is used in almost every industry, from healthcare to finance to education. It has made our lives easier and more efficient. We use IT to communicate with each other, access information, and manage our finances.
Components of Information Technology
IT is a broad field that encompasses many different components. The main components of IT are hardware, software, and networks.
- Hardwarerefers to the physical components of a computer system, such as the CPU, memory, and storage devices.
- Softwarerefers to the programs that run on a computer system, such as the operating system, applications, and drivers.
- Networksrefer to the connections between computers and other devices, such as printers and scanners.
Hardware Fundamentals: Intro To Information Technology Fbla
Hardware fundamentals encompass the physical components that constitute a computer system. These components play vital roles in processing, storing, and displaying information, enabling computers to perform their intended functions.
The harmonious interaction of hardware components is crucial for efficient and reliable computer operation. Each component serves a specific purpose, contributing to the overall functionality of the system.
Types of Hardware Components
- Processor (CPU):The brain of the computer, responsible for executing instructions and performing calculations.
- Memory (RAM):Stores data and instructions that are being actively processed by the CPU.
- Storage (HDD/SSD):Provides long-term storage for data, programs, and operating systems.
- Input Devices (Keyboard, Mouse):Allow users to interact with the computer and provide input.
- Output Devices (Monitor, Printer):Display or print information processed by the computer.
- Network Interface Card (NIC):Facilitates communication with other computers or devices over a network.
- Graphics Card (GPU):Processes and displays graphical content, essential for gaming, video editing, and other graphics-intensive tasks.
- Sound Card:Handles audio input and output, enabling sound reproduction and recording.
- Power Supply Unit (PSU):Provides electrical power to all hardware components.
Functions of Hardware Components
Each hardware component performs specific functions that contribute to the overall operation of the computer:
- Processor:Executes instructions, performs calculations, and controls the flow of data.
- Memory:Stores data and instructions temporarily, providing fast access for the CPU.
- Storage:Provides permanent storage for data, programs, and operating systems.
- Input Devices:Convert human input into digital signals that the computer can understand.
- Output Devices:Display or print processed information in a human-readable format.
- Network Interface Card:Transmits and receives data over a network.
- Graphics Card:Processes and displays graphical content.
- Sound Card:Manages audio input and output.
- Power Supply Unit:Converts AC power into DC power for the computer components.
Importance of Hardware Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Regular hardware maintenance is essential to ensure optimal performance and longevity of the computer system. This includes:
- Cleaning:Removing dust and debris from components to prevent overheating and malfunctions.
- Upgrading:Replacing or adding hardware components to improve performance or add new functionality.
- Troubleshooting:Identifying and resolving hardware issues to restore functionality.
Proper hardware maintenance and troubleshooting help prevent system failures, data loss, and costly repairs, ensuring the computer operates efficiently and reliably.
Software Applications
Software applications are programs that perform specific tasks for users. They can be classified into three main categories: operating systems, productivity software, and application software.
Operating systems are the foundation of any computer system. They manage the hardware and software resources of the computer, and they provide a platform for running other software applications.
Productivity Software
Productivity software is designed to help users create and manage documents, spreadsheets, presentations, and other types of files. Examples of productivity software include Microsoft Office, Google Workspace, and Apple iWork.
Application Software
Application software is designed to perform specific tasks, such as editing photos, playing games, or managing finances. Examples of application software include Adobe Photoshop, Microsoft Flight Simulator, and QuickBooks.
Importance of Software Updates and Security Measures
It is important to keep software applications up to date with the latest security patches. Security patches fix vulnerabilities that could allow attackers to gain access to your computer or data. You should also be careful about what software you install on your computer.
Only install software from trusted sources, and be sure to read the terms of service before installing any software.
Networking and Communications
Computer networks are systems that connect multiple computers and devices, allowing them to share resources, exchange data, and communicate with each other. Networks enable the transfer of information, such as files, emails, and multimedia, between connected devices.
There are various types of computer networks, each with its own characteristics and applications:
- Local Area Networks (LANs): LANs are typically used to connect devices within a limited physical area, such as a home, office, or school.
- Wide Area Networks (WANs): WANs connect devices over a larger geographical area, such as a city, region, or country.
- Metropolitan Area Networks (MANs): MANs are networks that span a metropolitan area, such as a city or town.
- Virtual Private Networks (VPNs): VPNs are private networks that are created within a public network, such as the internet, to provide secure communication between devices.
Network topologies refer to the physical arrangement of devices within a network. Common network topologies include:
- Bus topology: Devices are connected to a single cable, forming a linear network.
- Star topology: Devices are connected to a central hub or switch.
- Ring topology: Devices are connected in a closed loop, with each device connected to two other devices.
- Mesh topology: Devices are connected to multiple other devices, creating a fully connected network.
Network protocols are sets of rules and procedures that govern how devices communicate on a network. Common network protocols include:
- TCP/IP: The Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol suite is a set of protocols used for communication on the internet and other networks.
- Ethernet: Ethernet is a widely used protocol for local area networks.
- Wi-Fi: Wi-Fi is a wireless protocol that allows devices to connect to a network without the use of cables.
Network security is essential for protecting networks from unauthorized access, data breaches, and cyber threats. Network security measures include:
- Firewalls: Firewalls are network security systems that monitor and control incoming and outgoing network traffic.
- Intrusion Detection Systems (IDSs): IDSs monitor network traffic for suspicious activity and can alert administrators to potential threats.
- Encryption: Encryption is the process of converting data into a secret code to protect it from unauthorized access.
Network troubleshooting involves identifying and resolving network problems. Common network troubleshooting techniques include:
- Ping: Ping is a command used to test the connectivity between two devices on a network.
- Traceroute: Traceroute is a command used to trace the path of data packets through a network.
- Network monitoring tools: Network monitoring tools can provide real-time visibility into network performance and can help identify and resolve problems.
Data Management

Data management is the process of organizing, storing, and retrieving data. It is a critical aspect of information technology, as it ensures that data is accessible, reliable, and secure.
There are many different types of databases, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. The most common types of databases include relational databases, NoSQL databases, and object-oriented databases.
Relational databases are the most traditional type of database. They are based on the relational model, which represents data as a collection of tables. Each table contains a set of rows and columns, and each row represents a single entity.
NoSQL databases are a newer type of database that is designed to handle large amounts of data. NoSQL databases are not based on the relational model, and they can store data in a variety of formats.
Object-oriented databases are designed to store objects. Objects are data structures that contain both data and methods. Object-oriented databases are often used to store complex data, such as images, videos, and audio files.
Data storage is the process of storing data on a computer system. Data can be stored on a variety of media, including hard drives, solid-state drives, and optical discs.
Data retrieval is the process of accessing data from a computer system. Data can be retrieved using a variety of methods, including SQL queries, NoSQL queries, and object-oriented queries.
Data security is the process of protecting data from unauthorized access, use, disclosure, disruption, modification, or destruction. Data security is a critical aspect of information technology, as it ensures that data is kept confidential, reliable, and available.
Data Storage Techniques
- Direct Access Storage Devices (DASDs)
- Network Attached Storage (NAS)
- Storage Area Networks (SANs)
- Cloud Storage
Direct Access Storage Devices (DASDs) are storage devices that are directly attached to a computer. DASDs can be either hard drives or solid-state drives.
Network Attached Storage (NAS) is a storage device that is connected to a network. NAS devices can be accessed by any computer on the network.
Storage Area Networks (SANs) are high-performance storage networks that are used to connect storage devices to servers. SANs provide fast and reliable access to data.
Cloud Storage is a storage service that is provided over the Internet. Cloud storage providers store data on their own servers, and users can access their data from any computer with an Internet connection.
Data Retrieval Techniques
- Sequential Access
- Random Access
- Indexed Access
Sequential access is a data retrieval technique that reads data from a storage device in a sequential order. Sequential access is used for data that is stored on magnetic tape.
Random access is a data retrieval technique that reads data from a storage device in any order. Random access is used for data that is stored on hard drives and solid-state drives.
Indexed access is a data retrieval technique that uses an index to find data on a storage device. Indexed access is used for data that is stored in a database.
Data Security Techniques
- Encryption
- Authentication
- Authorization
- Auditing
Encryption is a data security technique that converts data into a form that cannot be read by unauthorized users. Encryption is used to protect data that is stored on computers and transmitted over networks.
Authentication is a data security technique that verifies the identity of a user. Authentication is used to prevent unauthorized users from accessing data.
Authorization is a data security technique that controls the access of users to data. Authorization is used to ensure that users can only access the data that they are authorized to access.
Auditing is a data security technique that tracks the access of users to data. Auditing is used to detect and prevent unauthorized access to data.
Information Security

Information security is the practice of protecting information from unauthorized access, use, disclosure, disruption, modification, or destruction. It is a critical aspect of any organization’s operations, as it helps to ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of information.
There are many different aspects of information security, including:
- Confidentiality:Ensuring that information is only accessible to authorized individuals.
- Integrity:Ensuring that information is accurate and complete.
- Availability:Ensuring that information is accessible when needed.
- Non-repudiation:Ensuring that the sender or receiver of information cannot deny their involvement.
Common Threats to Information Security, Intro to information technology fbla
There are many different threats to information security, including:
- Viruses:Malicious software that can damage or delete files and programs.
- Malware:Malicious software that can steal information or control a computer.
- Hacking:The unauthorized access of a computer system or network.
- Phishing:Scams that attempt to trick people into giving up their personal information.
- Spam:Unsolicited electronic messages, often used to spread viruses or malware.
Security Measures and Best Practices
There are many different security measures and best practices that can be used to protect information, including:
- Firewalls:Network security devices that block unauthorized access to a network.
- Anti-virus software:Software that detects and removes viruses.
- Strong passwords:Passwords that are difficult to guess and are not reused across multiple accounts.
- Two-factor authentication:A security measure that requires users to provide two forms of identification before accessing an account.
- Encryption:The process of converting information into a form that cannot be read without a key.
Ethical and Legal Issues
Information technology raises numerous ethical and legal concerns that must be addressed to ensure responsible and ethical use of technology. These issues include data privacy, intellectual property rights, and responsible use of technology.
Data privacy refers to the protection of personal information from unauthorized access or misuse. Individuals have the right to control how their personal data is collected, used, and shared. Laws such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) provide individuals with rights and protections related to their personal data.
Intellectual Property Rights
Intellectual property rights refer to the legal protection of original works, such as software, music, and literature. These rights grant the creators of original works exclusive rights to control the use and distribution of their works. Copyright, patents, and trademarks are common types of intellectual property rights.
Responsible Use of Technology
Responsible use of technology involves using technology in a manner that respects the rights of others and avoids harm. This includes avoiding the spread of misinformation, engaging in cyberbullying, or using technology to commit crimes.
Emerging Trends in Information Technology

The rapid evolution of information technology is continuously shaping the world around us. Emerging trends, such as cloud computing, artificial intelligence (AI), and the Internet of Things (IoT), are transforming the way we live, work, and interact with technology.
These advancements are not only influencing the IT industry but also impacting various sectors, including healthcare, finance, manufacturing, and transportation. Understanding these trends is crucial for professionals and individuals alike to stay ahead in the ever-evolving digital landscape.
Cloud Computing
Cloud computing refers to the delivery of computing services, such as servers, storage, databases, networking, software, analytics, and intelligence, over the internet (“the cloud”).
- Benefits:
- Scalability and flexibility
- Cost efficiency
- Increased collaboration
- Potential Impact:
- Increased adoption in businesses and organizations
- Emergence of new cloud-based applications and services
Artificial Intelligence (AI)
Artificial intelligence refers to the ability of machines to perform tasks that typically require human intelligence, such as learning, problem-solving, and decision-making.
- Types of AI:
- Machine learning
- Deep learning
- Natural language processing
- Potential Impact:
- Automation of tasks
- Improved decision-making
- Advancements in fields such as healthcare, finance, and manufacturing
Internet of Things (IoT)
The Internet of Things (IoT) refers to the network of physical devices, vehicles, home appliances, and other items embedded with electronics, software, sensors, and network connectivity, enabling them to collect and exchange data.
- Applications:
- Smart homes
- Industrial automation
- Healthcare monitoring
- Potential Impact:
- Increased connectivity and automation
- Improved efficiency and productivity
- New business models and opportunities
FAQ Overview
What is the purpose of Intro to Information Technology FBLA?
Intro to Information Technology FBLA provides students with a comprehensive understanding of the field, preparing them for further study and careers in information technology.
What topics are covered in Intro to Information Technology FBLA?
The course covers hardware fundamentals, software applications, networking and communications, data management, information security, ethical and legal issues, and emerging trends in information technology.
What are the benefits of taking Intro to Information Technology FBLA?
Students who complete Intro to Information Technology FBLA gain a solid foundation in information technology, develop problem-solving and critical thinking skills, and enhance their employability in the tech industry.