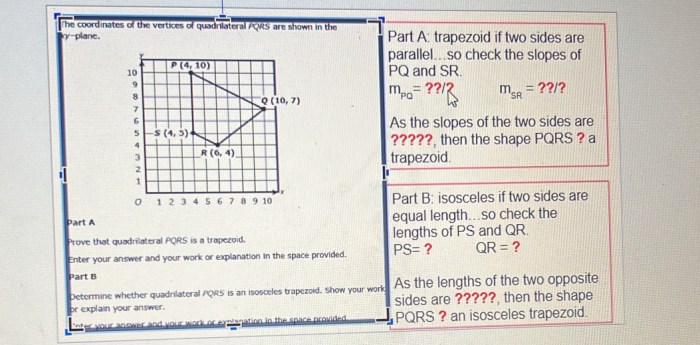
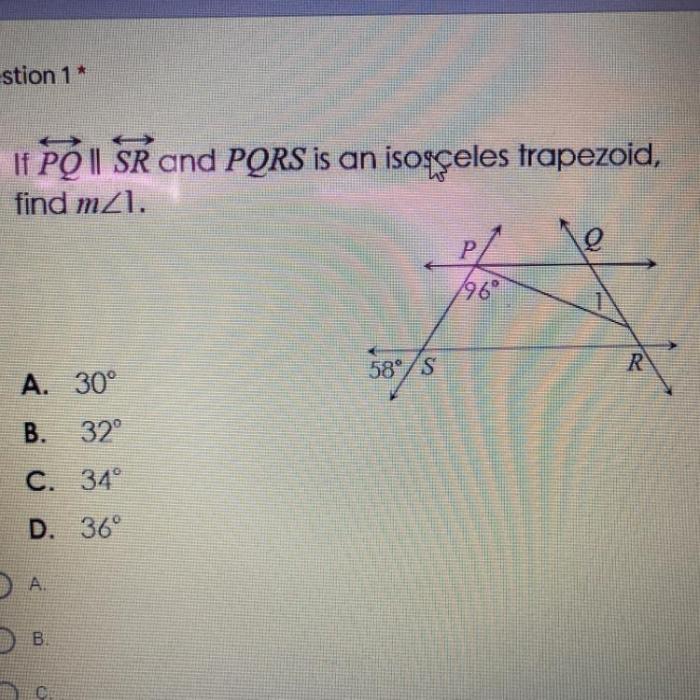
In trapezoid pqrs pq is parallel to sr – In the realm of geometry, the trapezoid stands out as a unique quadrilateral, characterized by its distinct parallel sides. Among the diverse properties that define a trapezoid, one intriguing aspect is the relationship between the parallel sides and the other elements of the shape, as exemplified by the statement “PQ is parallel to SR” in trapezoid PQRS.
This property not only influences the shape and measurements of the trapezoid but also reveals intriguing relationships between its angles and sides. Embarking on an exploration of this property, we will delve into the intricacies of trapezoid PQRS, uncovering the implications of parallel sides and their impact on the overall geometry of the figure.
Trapezoid
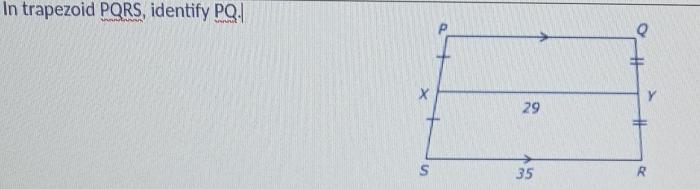
A trapezoid is a quadrilateral with one pair of parallel sides.
Identification of Parallel Sides
The parallel sides of a trapezoid are called the bases. The other two sides are called the legs. The bases are always longer than the legs.
Trapezoids can be classified into two types based on the orientation of their parallel sides:
- Right trapezoid:One of the legs is perpendicular to the bases.
- Oblique trapezoid:Neither leg is perpendicular to the bases.
Properties of Trapezoid PQRS
Given that PQ is parallel to SR, we have the following properties:
- The opposite angles are supplementary (i.e., they add up to 180 degrees): ∠PQR + ∠SRQ = 180° and ∠PQS + ∠QRS = 180°.
- The diagonals of the trapezoid are congruent (i.e., they have the same length): PQ = SR.
- The area of the trapezoid is given by the formula: Area = (1/2) × (PQ + SR) × PQRS.
Angle Relationships, In trapezoid pqrs pq is parallel to sr
In a trapezoid, the angles adjacent to the parallel sides are supplementary. This means that the sum of the two angles adjacent to a parallel side is always 180 degrees.
For example, in trapezoid PQRS, we have:
- ∠PQR + ∠SRQ = 180°
- ∠PQS + ∠QRS = 180°
Area and Perimeter
The area of a trapezoid is given by the formula:
Area = (1/2) × (PQ + SR) × PQRS
where PQ and SR are the lengths of the parallel sides and PQRS is the height of the trapezoid (the distance between the parallel sides).
The perimeter of a trapezoid is the sum of the lengths of all four sides:
Perimeter = PQ + SR + PQRS + SRQ
Question & Answer Hub: In Trapezoid Pqrs Pq Is Parallel To Sr
What is the defining characteristic of a trapezoid?
A trapezoid is a quadrilateral with exactly one pair of parallel sides.
How can we identify the parallel sides in trapezoid PQRS?
In trapezoid PQRS, PQ and SR are the parallel sides.
What is the relationship between the parallel sides and the other sides of a trapezoid?
The parallel sides are always congruent, while the non-parallel sides may or may not be congruent.