Plants of the Lewis and Clark Expedition: A Botanical Journey Through the American Frontier delves into the remarkable botanical discoveries made during the legendary expedition, shedding light on the rich plant life encountered, its cultural significance, and its lasting impact on the development of botany in the United States.
From the towering forests of the Pacific Northwest to the vast prairies of the Great Plains, Lewis and Clark meticulously documented hundreds of plant species, many of which were previously unknown to science. Their observations and collections not only expanded botanical knowledge but also provided invaluable insights into the ecological relationships and cultural practices of Native American tribes.
Common Plants Encountered
During the Lewis and Clark expedition, the explorers encountered a vast array of plant species, ranging from familiar species to those previously unknown to Europeans. These plants played a vital role in the expedition’s survival and provided valuable insights into the botanical diversity of the North American continent.
The expedition’s botanists, Meriwether Lewis and William Clark, meticulously documented the plants they encountered, categorizing them based on their uses. Edible plants, such as wild plums, chokecherries, and camas bulbs, provided sustenance for the explorers and their Native American guides.
Medicinal plants, including yarrow, mint, and echinacea, were used to treat illnesses and injuries.
Building materials, such as cottonwood and cedar, were essential for constructing shelters, boats, and other equipment. Lewis and Clark also encountered a variety of ornamental plants, such as wild roses and lupines, which added beauty to their surroundings.
Ethnobotanical Significance: Plants Of The Lewis And Clark Expedition
Plants held great cultural significance for the Native American tribes encountered by Lewis and Clark. Native Americans relied on plants for a wide range of purposes, including food, medicine, shelter, and spiritual practices.
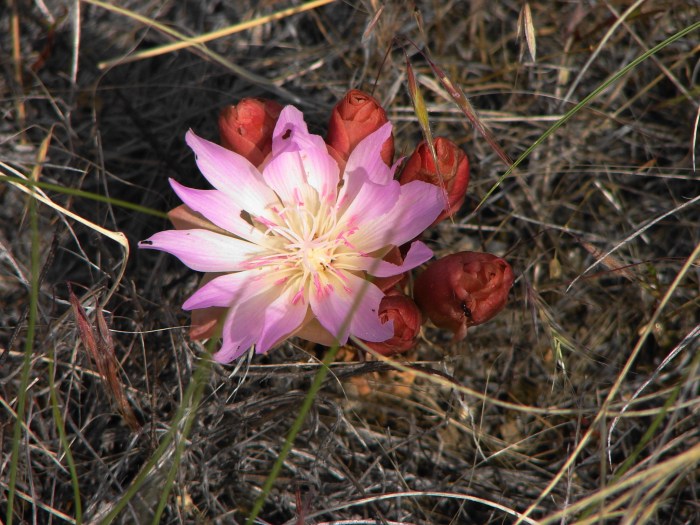
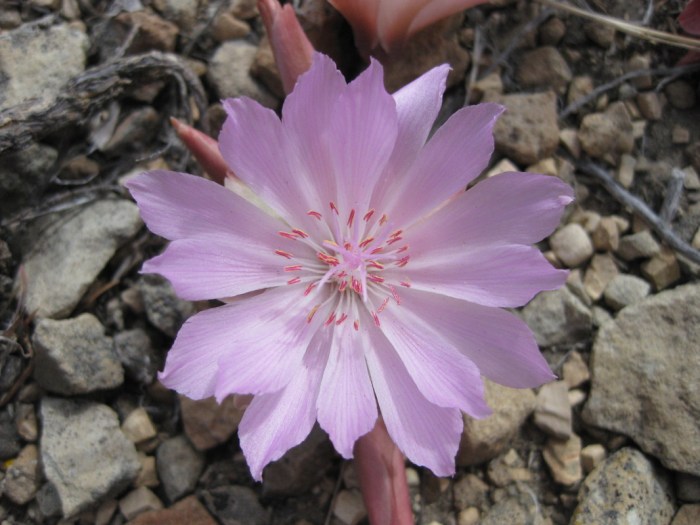
For example, the Nez Perce tribe used the roots of the bitterroot plant as a food source, while the Blackfeet tribe used the bark of the lodgepole pine to build their iconic tepees. Native Americans also possessed extensive knowledge of medicinal plants and used them to treat a variety of ailments, such as wounds, burns, and infections.
The expedition’s encounters with Native American tribes provided valuable insights into the cultural significance of plants and their traditional uses.
Botanical Observations

Lewis and Clark’s expedition made significant contributions to botanical knowledge through their detailed observations of plant life. They documented the morphology, habitats, and distributions of numerous plant species, many of which had never been scientifically described before.
Their observations included detailed descriptions of plant structures, such as leaves, flowers, and fruits, as well as notes on their environmental preferences and geographic ranges. These observations laid the foundation for future botanical research and contributed to the development of a more comprehensive understanding of North American flora.
Plant Collections and Specimens

Lewis and Clark collected and preserved a vast number of plant specimens during their expedition. They used a variety of methods, including pressing, drying, and storing in jars, to preserve the specimens for future study.
The plant specimens collected by Lewis and Clark were invaluable for botanical research and played a pivotal role in the development of botany in the United States. They provided the basis for the first comprehensive descriptions of many North American plant species and contributed to the understanding of plant diversity and distribution.
Ecological Impact

The Lewis and Clark expedition had both positive and negative ecological impacts on plant communities. The introduction of non-native species, such as dandelions and cheatgrass, had long-term effects on the composition and structure of plant communities.
Additionally, the expedition’s activities, such as grazing by horses and collecting plant specimens, may have had localized impacts on plant populations. However, the expedition also contributed to the conservation of plant species by raising awareness of their importance and documenting their distributions.
Frequently Asked Questions
What were some of the most important plant discoveries made by Lewis and Clark?
The expedition documented over 200 new plant species, including the western white pine, the bitterroot, and the camas lily. These discoveries significantly expanded the understanding of North American flora and contributed to the development of botany as a scientific discipline.
How did Native American tribes utilize plants during the Lewis and Clark expedition?
Native Americans played a crucial role in sharing their knowledge of plant uses with Lewis and Clark. They used plants for a wide range of purposes, including food, medicine, shelter, and clothing. For example, the Nez Perce tribe introduced the explorers to the camas lily, a nutritious bulb that became a staple food source.
What was the ecological impact of the Lewis and Clark expedition on plant communities?
The expedition introduced non-native plant species, such as dandelions and thistles, which have since become widespread in North America. Additionally, the expedition’s activities, such as logging and grazing, may have had localized impacts on plant populations.