When a cement block accidentally falls from rest, it embarks on an unanticipated journey governed by the laws of physics. This seemingly innocuous event triggers a chain reaction with far-reaching implications, demanding attention to safety measures and engineering considerations. Delving into the science behind this occurrence, we unravel the principles that dictate the block’s motion, assess the potential damage it may inflict, and identify strategies to mitigate risks associated with such incidents.
As the block succumbs to the relentless pull of gravity, it accelerates earthward, its velocity increasing with each passing moment. The impact it exerts upon landing depends on factors such as its mass, height of fall, and the nature of the surface it strikes.
Understanding these dynamics is crucial for preventing or minimizing damage to property and ensuring human safety.
1. Initial Conditions
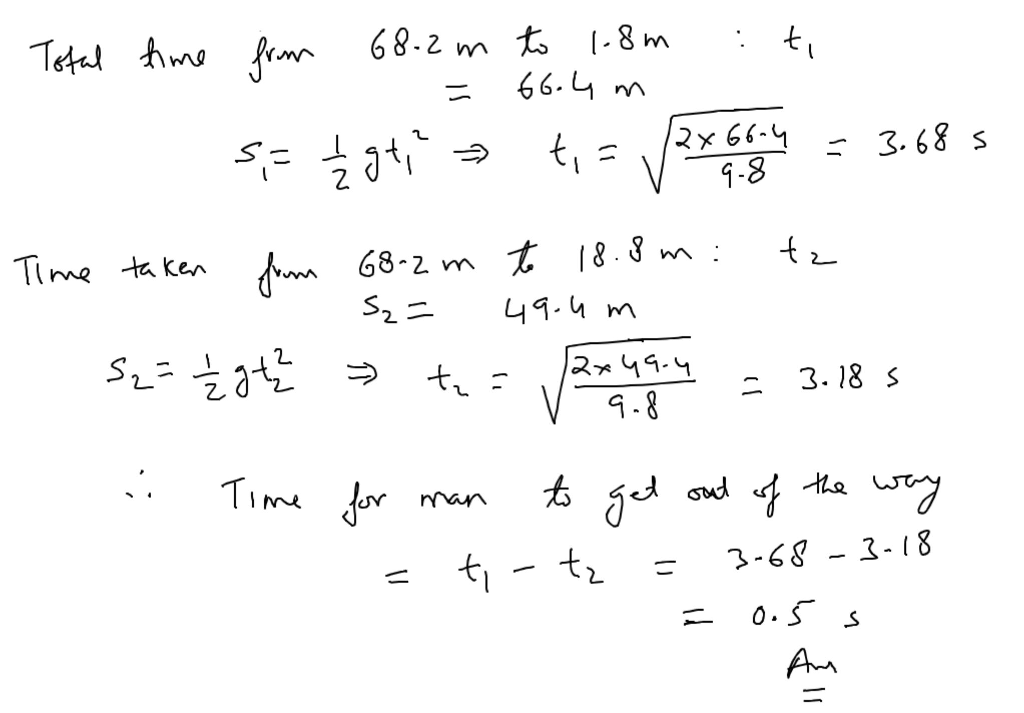
A cement block at rest is an object that is stationary and not moving. It is not subject to any external forces, such as friction or air resistance. This means that the block will remain at rest unless an external force is applied to it.
An illustration of a cement block at rest is a block sitting on a flat surface, not moving or being acted upon by any external forces.
2. Accidental Fall: A Cement Block Accidentally Falls From Rest
An accidental fall of a cement block can occur when the block is not properly secured or is subjected to an external force that causes it to fall. Potential causes of the fall could include:
- Inadequate support or improper installation
- Structural failure due to corrosion or deterioration
- Natural disasters such as earthquakes or high winds
- Human error or negligence
Examples of situations where a cement block could fall include:
- A stack of cement blocks collapsing due to improper stacking or overloading
- A cement block wall failing due to structural damage or poor construction
- A cement block falling from a height due to a loose or broken attachment
3. Physics of the Fall
When a cement block falls, it is subject to the force of gravity. Gravity is a force that attracts objects towards each other. The acceleration due to gravity on Earth is approximately 9.8 m/s 2.
The acceleration due to gravity causes the cement block to accelerate downwards. The acceleration is constant, meaning that the block will fall faster and faster as it falls.
| Concept | Formula | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Acceleration due to gravity | g = 9.8 m/s2 | The constant acceleration of an object falling towards the Earth |
| Distance fallen | d = 1/2
|
The distance an object falls in a given time |
| Velocity | v = g
|
The velocity of an object falling in a given time |
4. Consequences of the Fall
A falling cement block can cause significant damage to property and infrastructure. The severity of the damage depends on the size and weight of the block, the height from which it falls, and the surface it lands on.
Potential consequences of a falling cement block include:
- Damage to buildings, vehicles, or other structures
- Injury or death to people
- Blockage of roadways or other public spaces
- Disruption of utilities or services
Real-life examples of accidents involving falling cement blocks include:
- In 2021, a cement block fell from a construction site in New York City, killing a pedestrian
- In 2019, a cement block fell from a bridge in California, damaging a car and injuring the driver
- In 2018, a cement block fell from a building in London, causing extensive damage to a nearby store
5. Safety Measures

There are several safety measures that can be taken to prevent accidental falls of cement blocks. These measures include:
- Properly securing cement blocks during storage and transportation
- Ensuring that cement blocks are stacked securely and not overloaded
- Inspecting cement blocks regularly for signs of damage or deterioration
- Using proper lifting techniques when handling cement blocks
- Wearing appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) when working with cement blocks
The following checklist can be used to help prevent accidental falls of cement blocks:
- Inspect cement blocks before use for any damage or deterioration.
- Stack cement blocks securely and do not overload them.
- Use proper lifting techniques when handling cement blocks.
- Wear appropriate PPE when working with cement blocks.
- Store cement blocks in a safe and secure location.
6. Engineering Considerations
When designing structures involving cement blocks, it is important to consider the potential for accidental falls. This can be done by:
- Using proper engineering principles to design structures that are resistant to collapse
- Ensuring that cement blocks are properly installed and maintained
- Using engineering techniques to minimize the risk of block falls, such as using reinforcement or protective coatings
Examples of engineering techniques to minimize the risk of block falls include:
- Using reinforced concrete blocks
- Using steel reinforcement bars in cement block walls
- Applying protective coatings to cement blocks to prevent deterioration
Questions and Answers
What factors influence the severity of damage caused by a falling cement block?
The severity of damage depends on the block’s mass, height of fall, impact surface, and any protective measures in place.
What safety precautions can be taken to prevent accidental falls of cement blocks?
Proper storage, secure handling, and regular inspections are essential to minimize the risk of falls.
How do engineering principles contribute to reducing the risk of cement block falls?
Structural design, proper installation, and ongoing maintenance play a crucial role in ensuring the stability and integrity of structures involving cement blocks.